Guide To Electronics Potting
Electronics potting is a widely used method of protecting and encapsulating circuit boards and components, or entire devices in a protective material to protect them from moisture, dust and other contaminants.
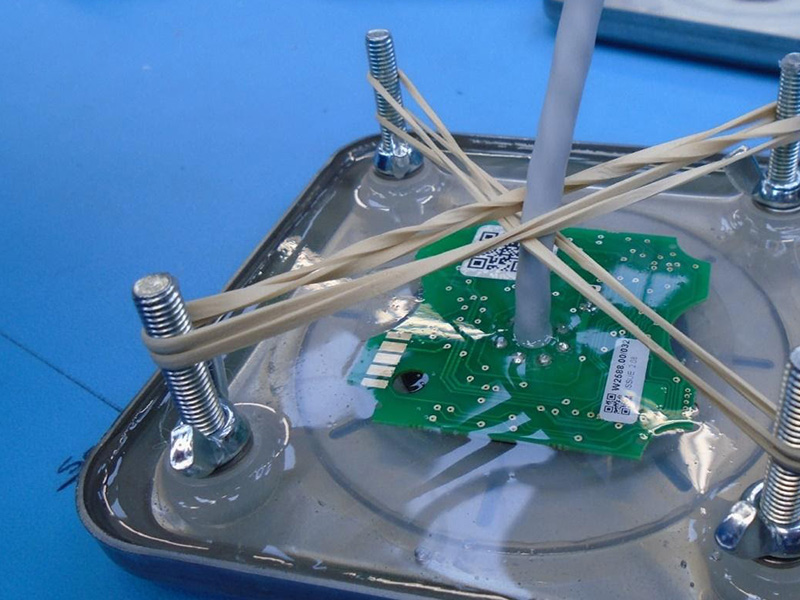
The circuit board is placed inside a pot and a solid or gelatinous liquid compound is poured into the pot, filling it and covering the PCB and the structure completely. Gelatinous compounds are used for high voltage assemblies and exclude gaseous phenomena such as corona discharge.
The liquid solidifies and the circuit board is encased inside the pot – this then becomes part of the end product. The solid coating helps protect the circuit board from shock and vibration and is used for the exclusion of water, moisture, or corrosive agents. It helps to ensure the quality of the product.
Potting can also provide additional mechanical support and improve heat dissipation.
Top tips to achieve outstanding potting
Prepare the workspace
Ensure that the workspace is clean, well-ventilated and free from distractions. Gather all necessary tools and materials, including the potting material, mixing container, mixing tool, vacuum chamber (if needed), and potting machine (if needed).
Choose the potting material
Choose a potting material that is compatible with the components and PCB being potted, as well as the intended application. Consider factors such as temperature range, chemical resistance, and electrical properties when selecting a potting material. Consult industry standards and guidelines for advice on appropriate materials for specific applications.
Prepare the potting material
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for preparing the potting material, including the mixing ratio and mixing time. Use only the recommended amount of potting material to ensure proper curing and avoid wastage.
Apply the potting material
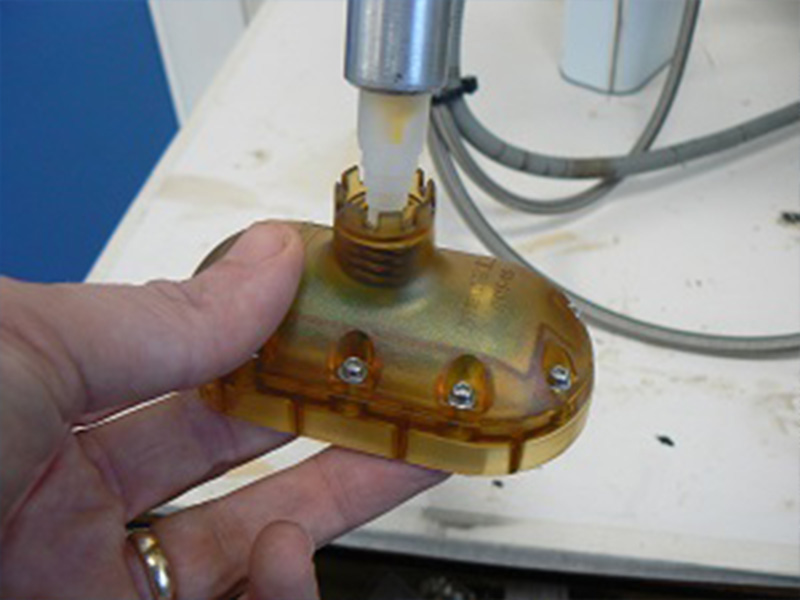
Use a vacuum chamber to remove any air bubbles from the potting material before applying it to the PCB or component, if necessary. Pour the potting material into the mixing container and then carefully pour it onto the PCB or component, making sure to cover all the sensitive parts. Use a potting machine, if available, to ensure accurate and consistent potting.
Cure the potting material
Allow the potting material to cure according to the manufacturer’s instructions, taking care to maintain the recommended temperature and humidity. Avoid moving or disturbing the potting material during the curing process, as this can cause defects.
Inspect the potting
Once the potting material has cured, inspect it to ensure that it is smooth and free of defects. Check for any voids, cracks, or other signs of incomplete potting that may affect the functionality of the device. If necessary, re-pot the component or PCB.
Clean up
After potting, clean up any excess potting material using a suitable solvent or scraping tool. Adhere to workplace safety guidelines when handling hazardous materials.
Remember to adhere to industry standards and guidelines when potting in a professional setting. By following these steps, you can ensure that your potted components and PCBs are protected from moisture, dust, and other contaminants and meet the required levels of quality and reliability.
Quality standards in potting
While IPC standards do not specifically cover potting, they may be relevant to potting processes in the electronics industry. For example, IPC-A-610, which covers the acceptability of electronic assemblies, includes criteria for inspecting potting materials, such as checking for voids or bubbles in the potting material that could impact the performance or reliability of the assembly.
Some of the industry standards that are particularly relevant to potting include the following:
IPC/JEDEC J-STD-020 – Moisture/Reflow Sensitivity Classification for Nonhermetic Solid State Surface Mount Devices
This standard establishes classifications for the moisture sensitivity of solid-state surface mount devices, which can be useful in evaluating the suitability of potting materials for specific applications where moisture resistance is critical.
Other relevant industry standards such as ASTM D635 (Standard Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent and Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position) provide guidance on various aspects of potting, including the suitability of potting materials, their flammability and moisture resistance and criteria for inspecting potting materials to ensure they meet industry standards for reliability and performance.
It’s important for professionals in the electronics industry to stay up-to-date with the latest industry standards and guidelines to ensure their work meets the required levels of quality and reliability.
The pros and cons of potting in PCB assembly
PROS
PCB potting is fast and easy to carry out. This makes it well suited for use on assembly lines and in high-volume manufacturing environments.
The robust, solid nature of potting makes it a good choice for products that require a significant degree of impact resistance – it will protect PCBs and products against mechanical shock and damage, delivering greater longevity.
Potting should also be considered if you are looking to prioritise vibration dampening, heat dissipation and privacy and security.
CONS
With regard to privacy and security, the nature of potting makes accessing your PCB and reverse engineering your product very difficult.
There are certain types of PCB assembly for which potting is not well suited. Owing to its structure and composition, it is not a good choice if there are any thickness, weight or size restrictions connected to your product, for example.
For the same reasons, repair work is very difficult to carry out on potted circuit boards.
Choosing the right coating for your PCB
The coating of printed circuit boards is an essential part of the product manufacturing process – it is integral to product performance and reliability. There are a number of PCB protective technologies available and the choice of PCB protective system is important.
The one you need depends on a number of manufacturing and market-use factors and the decision you make will have a direct impact on product quality and brand reputation.

We’re here to help
If you’re looking for a PCB supplier, ready and prepared to adapt to your specific or changing needs, please contact us at

PCB Assembly
Precise, reliable PCB assembly to your exact requirements.
Box Build Assembly
Optimise your supply chain with our turnkey assembly service.
